Internal DNS Cisco Host Table
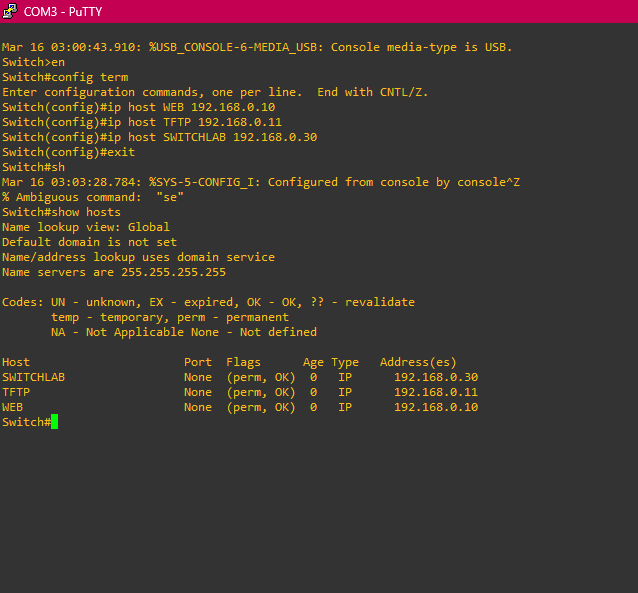
Internal DNS for Smaller Environments:
Creating hostname tables in Cisco routers and switches is a wise practice because it simplifies network management by allowing administrators to use human-readable hostnames instead of remembering IP addresses. This approach aids in troubleshooting, as hostnames are easier to identify in logs than numeric IPs, and improves network efficiency by allowing quick resolution of hostnames without relying on external DNS servers. Hostname tables ensure consistency across the network, reducing errors and confusion, and can enhance configuration and access control by enabling routers to apply settings based on hostnames. Additionally, they provide clear documentation, which is crucial as networks grow, making it easier to scale and manage devices with consistent naming conventions.
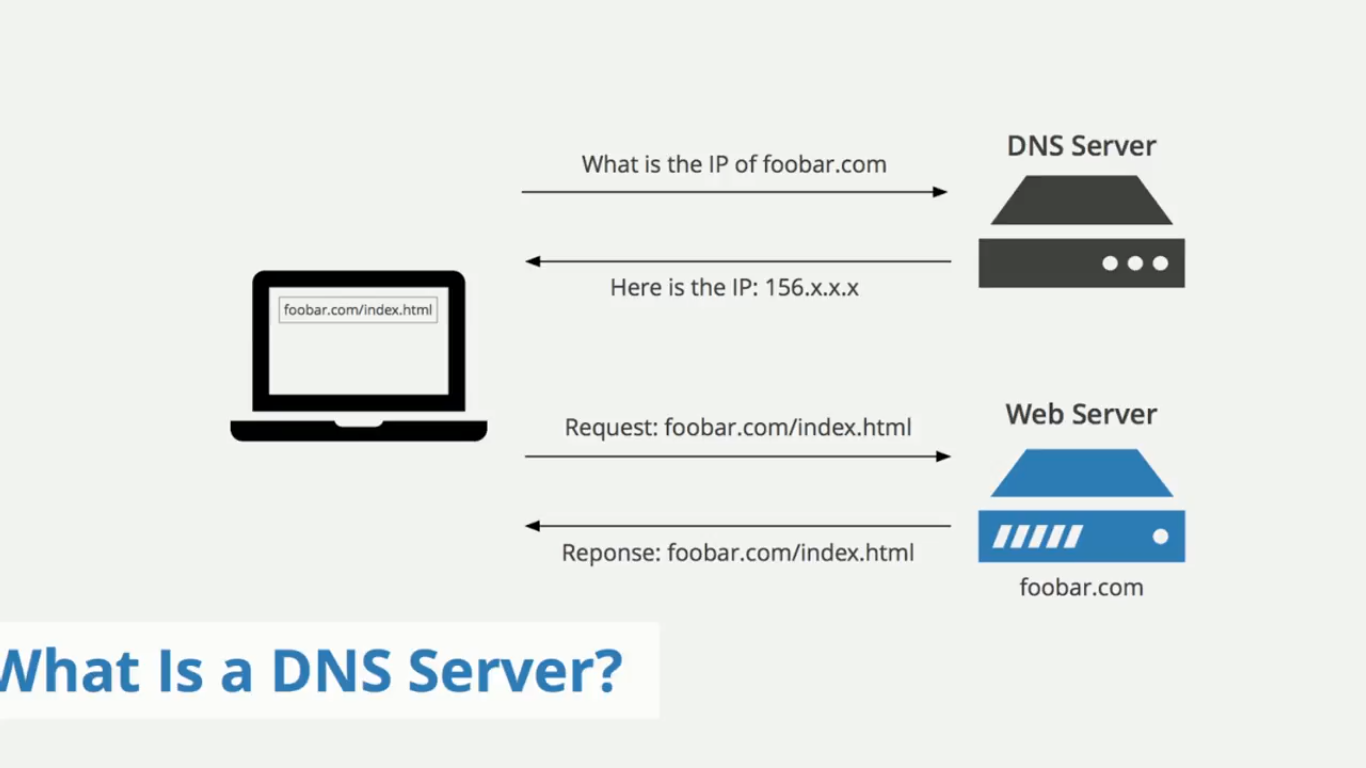
External DNS for Larger Environments:
In a larger network environment, using external DNS servers is smarter because it centralizes the management of hostname resolution, making it more scalable and efficient. As the network grows, manually managing hostname tables on each individual router becomes cumbersome and error-prone. External DNS servers allow all devices in the network to resolve hostnames consistently without the need for each router to maintain its own local mapping. This reduces the administrative burden, minimizes the risk of inconsistencies, and improves network performance by providing a reliable and centralized mechanism for name resolution. Additionally, DNS servers can provide redundancy, better fault tolerance, and faster resolution times, especially when implemented with caching, which significantly enhances overall network reliability and efficiency.
Project information
- Category Networking
- CompanyCisco
- Project date 17th March, 2025
- Visit Cisco Website